Reaction kinetic studies in a plug flow reactor
Procedure :
- Note down the concentration of ethyl acetate(EA) and NaOH in stock solution.
- Fill the reservoirs with NaOH and ethyl acetate stock solution.
- Calculate the volume of the tubular reactor.
- Switch on the pump and allow ethyl acetate to flow into the reactor at certain flowrate and measure the flowrate(vA) using rotameter.
- Set the required temperature to be maintained in the reactor. Switch on the heater to heat the reactor contents to the required temperature.
- Calculate the flowrate of NaOH ( VB ) required to keep the desired value of M( M = CBO/CAO ). M may be greater than or equal to one. Calculate the total flowrate (Q).
- Adjust the flowrate of NaOH to the calculated value, without changing the EA flowrate.
- Calculate the actual value of M obtained after adjusting the flowrates.
- Calculate the space time using the total flow rate.
- Start the stirrer in the reactor. Close the drain valve completely. Allow the reaction to proceed till steady state is attained, as indicated by constant reading in the conductivity meter.
- Note down the conductivity (in mS/cm) of the reaction mixture in, after steady state is attained. Note: Some conductivity meters may display conductance (mS) not the conductivity(mS/cm) [Refer theory for more information].
- Determine the concentration of unreacted NaOH in the reaction mixture by using the conductivity meter calibration equation.
- Repeat steps (6) to (12) for different EA flowrates .
- Conduct the experiment at different temperatures.
Observations and calculations:
A -> Ethyl acetate
B -> NaOH
Strength of Ethyl acetate in stock solution = CAS = ------------------------ gmol/L
Strength of NaOH in stock solution = CBS = ------------------------ gmol/L
Diameter of the tube ,d = -----------------------cm
Coil diameter , Dc =
cm
Number of turns= Nt =
V = volume of tubular reactor = ( d2/4)×
Dc Nt =
= -----------------------cm3
V =----------------------- L
Tabular columns:
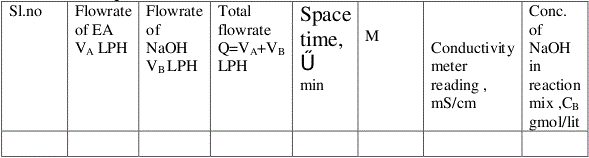
Calculations :
Calculate the total flow rate Q = VA + VB = LPM
Calculate the space time , = V/Q = min
Set value of M =
Concentration of ethyl acetate in the feed mixture,
CAo = --------------------gmol/L
Concentration of NaOH in the feed mixture,
CBo = --------------------gmol/L
As the conductivity meter calibration is available only at 28°C, the conductivity
meter reading obtained at a given temperature of reaction is to be corrected for 28°C.
Temperature compensation for conductivity meter
Where ,
YT =conductivity meter reading at any temperature T in mS/cm
Y28 = conductivity meter reading at a temperature of 28°C in mS/cm
Obtain Y28 corresponding to measured conductivity meter reading ( YT) using the equation above.
Conductivity meter is calibrated for concentrations of NaOH in the reaction mixture at a temperature of 28°C.
Obtain the Concentration of NaOH at 28°C using the calibration equation given below Conductivity meter calibration equation for 28°C.
Where,
CB= Concentration of NaOH in the reaction mixture at steady state
Y28 = Conductivity meter reading for solution, corrected for 28°C
Concentration of unreacted NaOH in the reaction mixture at steady state,
CB= gmol/L (obtained from the conductivity meter calibration graph)
Concentration of ethyl acetate in the reaction mixture at steady state,
CA= --------------------gmol/L
Conversion of ethyl acetate,
(CA/ CAo)=
Performance equation for PFR with rate equation of the form
for M>1 , can be written as
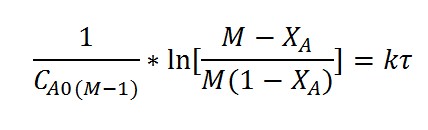
Plotting
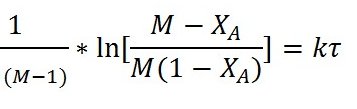 Vs
Vs 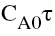 yields a straight line passing through
yields a straight line passing through
origin if the assumed rate equation is correct. The slope=k.
For M=1, the performance equation is 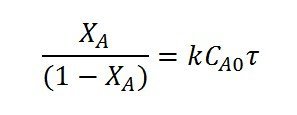
So the plot of 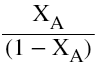 vs
vs 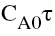
yields a straight line passing through origin. The slope=k.
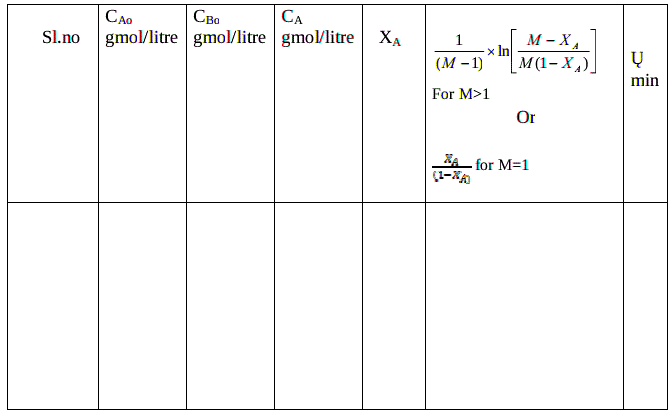
Graph for M >1
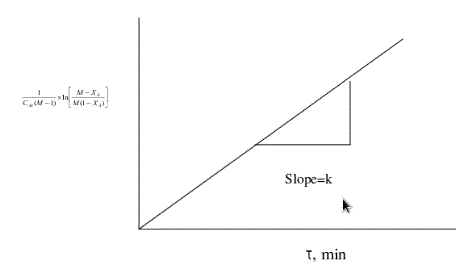
From the graph we get,
Slope = k =..............
L/(g mole. min)
Similarly the experiment may be performed with different temperatures and the
rate constants at these temperatures may be determined.
Obtain the rate constant at three or more different temperatures.

From Arrhenius Equation,
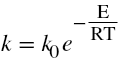
Plot lnk vs 1/T
Determine the activation energy (E) and the frequency factor (ko) from the slope and intercept of the above plot.
Intercept= lnk0
Slope=-E/R
R is the gas constant
Frequency factor , ko=min-1(litre / gmol)
Activation energy= E=
J/mol
Results :
The rate constant for the saponification of Ethy acetate with NaOH at a temp of
ToC,
k = -------------------------------litre/((mol)(min))
Discuss and conclude on the temperature dependency of rate constant.
The activation energy (E) for the reaction=J/mol
The frequency factor (ko)=
min-1(litre / gmol)
